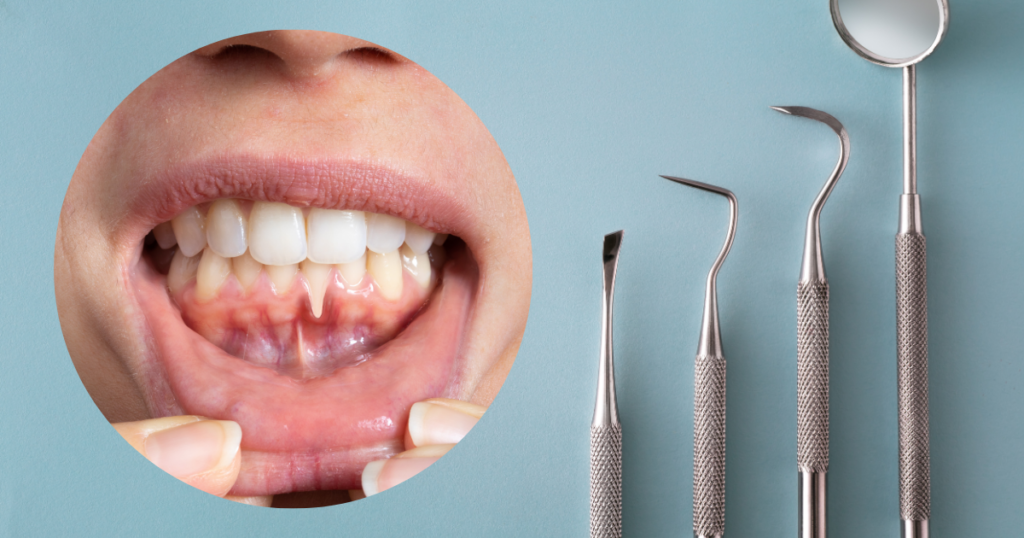
Gum recession is a common dental problem that many people don’t notice until it becomes serious. It happens when the gum tissue surrounding your teeth gradually pulls back or wears away, exposing more of the tooth or even its root. This not only affects how your smile looks but can also lead to tooth sensitivity, discomfort, and long-term oral health issues if left untreated.
Understanding gum recession treatment options early can help protect your teeth and prevent permanent damage. Whether your condition is mild or advanced, there are effective ways to manage and even restore your gum health.
What Is Gum Recession?
Gum recession occurs when the protective gum tissue surrounding the teeth begins to shrink or pull away. When this happens, small gaps form between the teeth and gums where bacteria can easily collect. Over time, this can damage supporting bone and lead to tooth loss if not properly treated.
Many people first notice gum recession when their teeth appear longer than usual or when they feel sensitivity while eating hot, cold, or sweet foods.
Healthy gums should fit snugly around each tooth, forming a protective barrier against bacteria. If you’re unsure what healthy gum tissue should look like, you may find it helpful to read Healthy Gums: Your Guide to Strong and Lasting Oral Health to understand the signs of proper gum health.
Common Signs of Receding Gums
Recognizing symptoms early makes treatment easier and more effective. Watch for these common signs:
- Teeth that look longer than before
- Tooth sensitivity, especially near the gumline
- Visible tooth roots
- Pain or discomfort near the gums
- Bleeding during brushing or flossing
- Loose teeth in advanced cases
Some people also experience swelling or redness in the affected area. If inflammation is present, you may want to explore Swollen Gums: Causes, Symptoms, and How to Reduce Gum Inflammation Naturally to understand how gum irritation develops and how to control it.
What Causes Gum Recession?
There isn’t just one cause of gum recession. It often occurs as a result of multiple contributing factors rather than a single cause.
1. Aggressive Brushing
Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristle toothbrush can slowly damage delicate gum tissue. Over time, this repeated pressure causes the gums to wear away and pull back from the teeth. Many people think brushing harder cleans better, but it actually increases the risk of gum recession. Using gentle pressure and a soft-bristled brush helps protect your gums while still keeping teeth clean.
2. Gum Disease
One of the most common causes of receding gums is periodontal disease. This bacterial infection attacks the gum tissue and gradually damages the bone that supports the teeth. As the infection progresses, the gums begin to separate from the teeth, creating pockets where more bacteria can grow. Without treatment, this process can lead to severe gum loss and even tooth loss.
3. Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up along the gumline. Over time, plaque hardens into tartar, which can only be removed through professional dental cleaning. Tartar irritates the gums and causes inflammation, leading them to pull away from the teeth. Maintaining consistent oral hygiene is essential to prevent this chain reaction.
4. Genetics
Some people are naturally more prone to gum recession due to inherited traits. Thin or delicate gum tissue may recede more easily, even with proper oral care. If gum problems run in your family, regular dental checkups become even more important. Early monitoring can help manage issues before they become severe.
5. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can make gum tissue more sensitive and reactive to irritation. This is especially common during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. Increased sensitivity makes gums more vulnerable to inflammation and recession if not properly cared for. Paying extra attention to oral hygiene during these periods can help reduce risk.
6. Teeth Grinding or Clenching
Constant grinding or clenching places excessive force on teeth and their supporting structures. This pressure can weaken the gums and cause them to recede over time. Many people grind their teeth during sleep without realizing it. Dentists often recommend night guards to protect teeth and reduce stress on gum tissue.
7. Tobacco Use
Smoking and other forms of tobacco use significantly harm gum health. Tobacco reduces blood flow to the gums, which limits oxygen and nutrients needed for healing. It also weakens the immune response, making it harder to fight infection. As a result, gum damage progresses faster, and recovery becomes more difficult.
8. Misaligned Teeth
Teeth that are not properly aligned can create uneven pressure on certain areas of the gums. This constant stress can gradually wear down gum tissue around specific teeth. Misalignment also makes cleaning more difficult, increasing plaque buildup. Correcting alignment can help distribute pressure evenly and protect gum health.
Understanding the underlying cause of gum recession helps dental professionals choose the most effective treatment plan and prevent further damage.
Why Gum Recession Should Not Be Ignored
Many people think receding gums are only a cosmetic concern, but the risks go much deeper.
- Increased tooth sensitivity
- Higher risk of cavities on exposed roots
- Gum infections
- Bone loss around teeth
- Tooth loosening or loss
In severe cases, untreated gum recession can permanently damage oral structures. That’s why early treatment is always recommended.
Non-Surgical Gum Recession Treatment Options
Mild to moderate gum recession can often be treated effectively without the need for surgery. These treatments are designed to control infection, reduce sensitivity, and prevent the condition from getting worse. Early intervention is important because non-surgical methods work best before significant tissue loss occurs. With proper care and professional guidance, many people can stabilize their gum health and avoid invasive procedures.
Professional Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing)
Scaling and root planing is a specialized dental cleaning that goes deeper than routine cleaning. It removes plaque and hardened tartar from below the gumline, where harmful bacteria tend to collect. The tooth roots are then smoothed, making it harder for bacteria to attach and easier for the gums to heal and reattach to the teeth. This treatment is often the first step in managing gum recession caused by gum disease.
Desensitizing Treatments
When gum tissue recedes, exposed tooth roots can become extremely sensitive to hot, cold, or sweet foods. Dentists may apply desensitizing agents that help block nerve signals and reduce discomfort. These treatments also provide a protective layer over exposed areas, helping to prevent further irritation. Regular use of desensitizing products at home may also be recommended for continued relief.
Antibiotic Therapy
If gum recession is linked to bacterial infection, antibiotic treatment may be necessary. Dentists may use topical antibacterial gels, medicated rinses, or, in some cases, oral antibiotics to control harmful bacteria. Reducing infection helps calm inflammation and allows gum tissue to heal more effectively. Antibiotic therapy is often combined with deep cleaning for better long-term results.
Orthodontic Treatment
Misaligned teeth can place uneven pressure on certain areas of the gums, contributing to tissue breakdown over time. Orthodontic treatment helps reposition teeth into proper alignment, reducing stress on the surrounding gum tissue. By correcting the bite and improving tooth positioning, this approach can prevent further recession and make oral hygiene easier. In some cases, orthodontic care is an important part of long-term gum health management.
Improved Oral Hygiene Routine
Gentle brushing, flossing, and proper dental care are essential to stop progression.
If your gums bleed during brushing, addressing that problem early can prevent worsening recession. You may benefit from reading How to Stop Bleeding Gums: Proven Solutions for Healthy Gums for practical care tips.
Surgical Gum Recession Treatment (Advanced Cases)
When gum loss becomes severe, surgical treatment may be necessary to restore tissue and protect teeth.
Gum Grafting
This is the most common procedure for receding gums. Tissue is taken from another area (often the roof of the mouth) and attached to the affected area to cover exposed roots.
Pinhole Surgical Technique
A minimally invasive method where tiny holes are made in the gum to reposition existing tissue over exposed roots.
Regenerative Procedures
If bone loss has occurred, special materials may be used to encourage tissue and bone regrowth.
Surgical treatment not only improves appearance but also protects teeth from long-term damage.
Can Receding Gums Grow Back Naturally?
This is one of the most frequently asked questions. Unfortunately, gum tissue does not grow back on its own once it has receded significantly.
However, early intervention can:
- Stop the further recession
- Improve gum attachment
- Reduce inflammation
- Protect exposed tooth roots
In mild cases, good oral care and professional treatment can stabilize the condition and prevent worsening.
Home Care Tips to Support Gum Healing
While professional treatment is important, daily habits play a major role in recovery and prevention.
Choose a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush
Use a soft-bristle toothbrush to protect your gums from unnecessary irritation. Hard bristles or aggressive brushing can wear down delicate gum tissue and make recession worse over time. Brush gently using small circular motions rather than scrubbing back and forth. This technique cleans effectively while keeping your gums safe from damage.
Keep Up a Consistent Oral Hygiene Routine
Maintaining daily oral care is essential for preventing further gum problems. Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss carefully to remove plaque between teeth where a toothbrush can’t reach. Skipping regular cleaning allows bacteria to build up along the gumline, increasing inflammation and infection risk. Consistency is more important than intensity — gentle, regular care keeps gums healthier long term.
Rinse with an Antibacterial Mouthwash
An antibacterial mouthwash helps reduce harmful bacteria that contribute to gum disease and plaque buildup. It reaches areas that brushing and flossing may miss, offering an extra layer of protection. Regular use can help control inflammation and keep the gumline cleaner. Choose an alcohol-free formula if you have sensitive gums to avoid dryness or irritation.
Stay Away from Tobacco in All Forms
Tobacco use significantly weakens gum health and slows the body’s natural healing process. Smoking reduces blood flow to gum tissue, making it harder for your mouth to fight infection and repair damage. It also increases the risk of gum disease, which is a major cause of gum recession. Quitting tobacco can greatly improve treatment results and overall oral health.
Support Gum Health with a Nutrient-Rich Diet
What you eat plays an important role in how well your gums heal and stay strong. Nutrients like vitamin C help repair tissue and reduce inflammation, while calcium supports strong teeth and bone structure. A balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins strengthens your body’s ability to fight infection. Proper nutrition not only benefits your gums but also improves overall oral health stability.
Manage Teeth Grinding
Teeth grinding or clenching can put extra stress on your gums and teeth, contributing to recession. Using a night guard, if recommended by your dentist, can help protect your teeth and reduce pressure on gum tissue. This simple step supports long-term gum and tooth health.
These habits support any gum recession treatment plan and help maintain long-term results.
When to See a Dentist
You should seek professional evaluation if you notice:
- Persistent tooth sensitivity
- Visible gum shrinkage
- Bleeding or swollen gums
- Pain while chewing
- Loose teeth
Early diagnosis makes treatment simpler, less invasive, and more effective.
Preventing Future Gum Recession
Prevention is always easier than treatment. Protect your gums with these simple steps:
- Brush gently with proper technique
- Schedule regular dental checkups
- Treat gum inflammation promptly
- Wear a mouthguard if you grind your teeth
- Maintain good nutrition and hydration
Consistent care is the best defense against receding gums.
Long-Term Outlook After Treatment
With proper care, most people achieve excellent results after gum recession treatment. The key is maintaining good oral hygiene and following your dentist’s recommendations.
Treated gums can remain stable for many years, and surgical procedures often provide permanent coverage of exposed roots. Regular monitoring ensures that any new issues are addressed quickly.
Final Thoughts
Gum recession is a serious oral health issue, but it is highly treatable when addressed early. Whether caused by brushing habits, gum disease, or other factors, timely intervention can prevent complications and protect your smile.
From professional cleanings to advanced surgical procedures, modern dentistry offers many effective options for a successful receding gums fix. Pairing treatment with good daily habits ensures long-term gum health and comfort.
If you notice changes in your gums, don’t ignore them. Early care can make the difference between simple treatment and complex dental procedures. Healthy gums are the foundation of strong teeth — and they deserve your attention.